Forests and Nature: The Heartbeat of Our Planet 🌿

forest
Climate
Nature
Ecosystem
Nature is the original architect of life. From the towering trees of the Amazon rainforest to the mossy undergrowth of temperate woodlands, forests are essential ecosystems that sustain life, regulate our climate, and provide a sanctuary for biodiversity. Yet, despite their importance, they continue to face increasing threats from human activity and environmental changes.
1. Forest Coverage and Global Distribution
Forests currently cover about 4.06 billion hectares of Earth’s land surface—around 31% of the total land area.
Types of forests:
- 🌳 Tropical forests – Dense, diverse ecosystems near the equator (e.g., Amazon, Congo).
- 🌲 Temperate forests – Found in regions with four seasons.
- 🌿 Boreal forests (Taiga) – Located in cold northern regions like Russia and Canada.
📊 Top 5 countries by forest area:
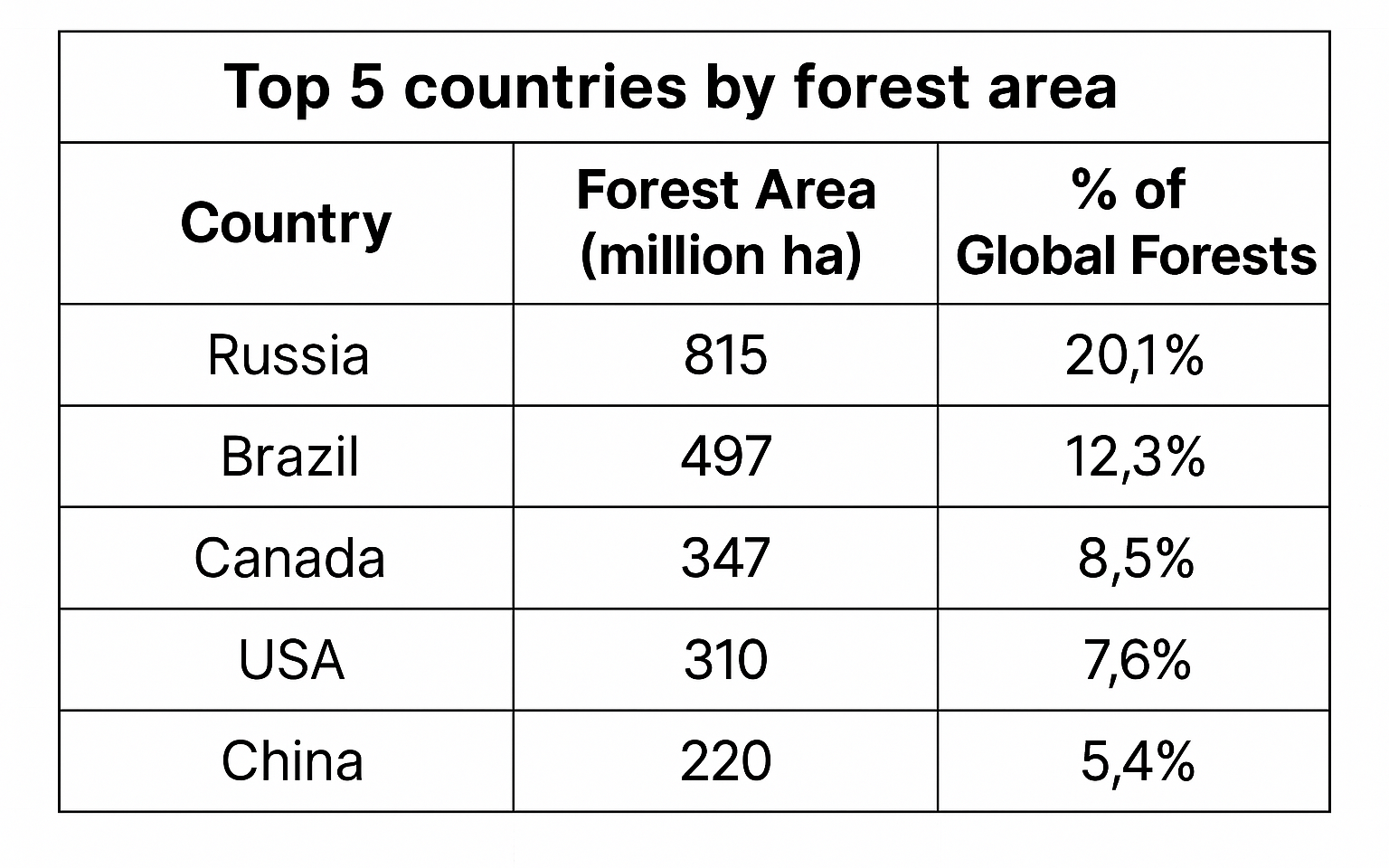
top 5 countries by forest area
🌬️ 2. Forests and the Climate: Carbon Sinks of the Earth
Forests absorb around 2.6 billion tons of CO₂ every year, helping mitigate climate change by removing greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
🌱 Key Fact: The Amazon Rainforest stores more than 100 billion metric tons of carbon.
🔥 But deforestation has the opposite effect. When trees are cut down or burned:
- CO₂ is released.
- Soil erodes.
- Local weather patterns are disrupted.
🧯 2023 Wildfire Stats:
- Global forest fires emitted 6,687 megatons of CO₂.
- Canada alone lost 18.5 million hectares of forest to wildfires—its worst year on record.
🐘 3. Biodiversity: Nature's Web of Life
Forests are home to 80% of the world’s terrestrial species. These include:
- Jaguars in South America
- Orangutans in Indonesia
- Tigers in India
- Countless plants, insects, and fungi yet to be discovered
📉 Biodiversity Crisis:
- Over 44,000 species are at risk of extinction.
- One million species could vanish within decades if current trends continue (UN IPBES Report).
💧 4. Water Cycle and Ecosystem Services
Forests act as natural water factories:
- Their roots absorb rainfall and prevent runoff.
- Forests replenish 75% of the world's freshwater.
Cities like New York, Bogotá, and Melbourne depend on forest watersheds for clean drinking water, saving millions in filtration costs.
👨👩👧 5. People and Forests
Indigenous Communities:
- Around 70 million Indigenous people live in or near forests.
- They are often the best stewards of the land, practicing sustainable harvesting and forest care.
Livelihoods:
- 1.6 billion people depend on forests for food, income, and shelter.
- Non-timber products like berries, mushrooms, honey, and herbal medicine support local economies.
6. Human Health and Mental Wellness
Studies show that time in nature can:
- Lower stress and anxiety
- Reduce blood pressure
- Improve focus and creativity
🌿 Forest bathing (Japanese: Shinrin-yoku) is a therapeutic practice where individuals immerse themselves in a forest environment for health benefits.
🚨 7. Deforestation: A Global Emergency
🌍 Every year, the planet loses over 10 million hectares of forest, roughly the size of Portugal.
Main drivers of deforestation:
- 🐄 Cattle ranching (especially in the Amazon)
- 🌾 Soy and palm oil farming
- 🌲 Logging (often illegal)
- 🏗️ Urban development
🌱 8. Restoration and Solutions
International Efforts:
- 🌳 The Bonn Challenge: aims to restore 350 million hectares of degraded land by 2030.
- 🌐 UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration (2021–2030)
9. Forests and Climate Resilience: Nature’s Shield
Forests don’t just store carbon they help societies adapt to climate change.
How Forests Build Resilience:
- Flood Prevention: Tree roots reduce surface runoff and absorb excess rainwater, lowering flood risks.
- Temperature Regulation: Urban forests and green belts cool cities by several degrees, reducing heatwaves.
- Soil Protection: Forest cover prevents erosion, landslides, and desertification.
- Storm Mitigation: Coastal mangroves act as natural barriers against cyclones and tsunamis.
💡 Example: After Cyclone Amphan in 2020, areas with intact mangroves in West Bengal experienced far less damage than deforested regions.
🐦 10. Forests and Wildlife Corridors: Preserving Ecosystems
Fragmentation of forests is a major threat to wildlife. Large, continuous forest areas are essential for species migration, breeding, and survival.
Wildlife Corridors:
- India: The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve connects tiger populations between multiple forests.
- Africa: The Kavango-Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area supports elephants and big cats across five countries.
- South America: Amazonian corridors ensure jaguars and tapirs move safely across territories.
Protecting corridors reduces human-wildlife conflict and preserves biodiversity.
Success Story:
In India’s Nilgiris, community-based projects are reviving native forests destroyed by tea plantations, restoring wildlife and water balance.
What You Can Do
- 🌱 Plant native trees
- 🛍️ Choose sustainable wood and paper products
- 🍽️ Reduce meat consumption (especially beef)
- 💚 Support Indigenous rights and forest-friendly policies
- 🌏 Educate others and spread awareness
Final Words
Forests and nature aren’t just beautiful—they are essential. They breathe life into our planet, hold ancient wisdom, and offer solutions to the world’s biggest crises. Protecting them isn’t just an environmental cause—it’s a human necessity.

